When comparing the four main combustion methods for treating VOCs, it's essential to analyze them based on several performance metrics, including temperature ranges, efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. Here's a breakdown of each method across the key factors:

Standard Operating Temperature: High, typically 850–1,200°C (1562–2192°F). The flame temperature is maintained to ensure complete combustion.
VOC Removal Efficiency: High (typically 98–99%), as the high temperatures break down VOCs effectively.
Deodorization Efficiency: Good, as the high temperatures also help eliminate odors.
NOx Generation: Potential for high NOx emissions due to the high operating temperatures.
CO Decomposition: Efficient, as the combustion process inherently decomposes CO into CO₂.
Heat Recovery Efficiency: Low, as the heat generated is not typically recovered.
Initial Costs: Moderate to high. Equipment costs can be high due to the need for durable materials that can withstand extreme temperatures.
Maintenance and Operating Costs: High. Regular maintenance is needed due to the high wear and tear from the intense heat, and fuel costs can be substantial.
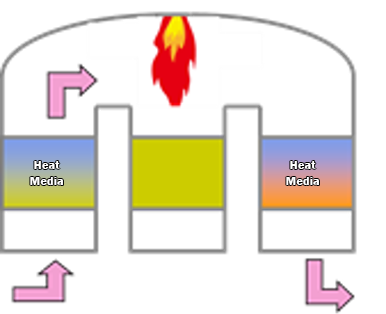
Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO)
Standard Operating Temperature: Typically 700–1,000°C (1292–1832°F).
VOC Removal Efficiency: Very high (typically 99.x%%).
Deodorization Efficiency: Good, since RTOs operate at high temperatures.
NOx Generation: Moderate, as the high temperatures can generate NOx but typically less than DFIs due to better temperature control.
CO Decomposition: Effective at breaking down CO into CO₂.
Heat Recovery Efficiency: High, as RTO systems use ceramic media to store and recover heat, making them more energy-efficient.
Initial Costs: High. The regenerative media and high-quality construction materials contribute to the initial cost.
Maintenance and Operating Costs: Moderate. While maintenance costs are lower than DFIs, periodic cleaning and maintenance of the heat recovery system are still required.

Catalytic Combustion System (CCS/CATox/CO)
Standard Operating Temperature: Low to moderate, typically 300–500°C (572–932°F), depending on the catalyst.
VOC Removal Efficiency: Very high (typically 99.x%%), but can be sensitive to the type of VOCs and oxidation catalyst efficiency.
Deodorization Efficiency: Very good, as catalyctic oxidation is highly effective at eliminating odors.
NOx Generation: None. Low combustion temperature, no generation of thermal NOx.
CO Decomposition: Efficient.CO is typically decomposed into CO₂ in the presence of the catalyst.
Heat Recovery Efficiency: Moderate, as heat recovery is not a primary function of this system.
Initial Costs: Moderate. Need to select efficient oxidation catalysts, but overall equipment costs are lower than those of RTOs and DFIs.
Maintenance and Operating Costs: Moderate. While there's no need for high operating temperatures, catalyst replacement or regeneration requires cost considerations.
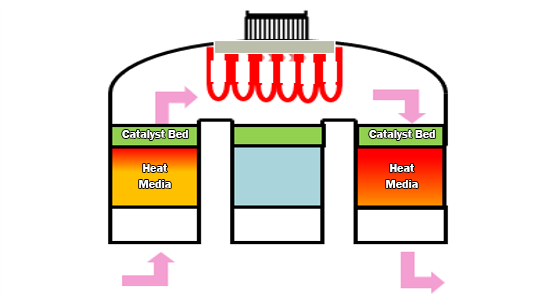
Regenerative Catalytic Oxidizer (RCO)
Standard Operating Temperature: Low to moderate, typically 300–600°C (572–1112°F).
VOC Removal Efficiency: Very high (typically 99.99x%).
Deodorization Efficiency: Very good, as catalytic oxidation is highly effective at eliminating odors.
NOx Generation: None, similar to catalytic combustion, with reduced NOx emissions.
CO Decomposition: Efficient.CO is oxidized into CO₂ with the catalyst.
Heat Recovery Efficiency: Very high, as RCOs combine both catalytic oxidation and regenerative heat recovery. This allows for efficient energy use and reduced operational costs.
Initial Costs: High. Due to the need for both catalytic materials and heat recovery systems.
Maintenance and Operating Costs: Moderate to low. Catalysts last longer than in CCS and generally require less maintenance, and heat recovery reduces overall energy consumption.
Summary Comparison Table
Feature | DFI | RTO | CCS/CATox/CO | RCO |
Operating Temperature | 850–1,200°C | 700–1,000°C | 300–500°C | 300–600°C |
VOC Removal Efficiency | 98–99% | 99.x% | 99.x% | 99.99x% |
Deodorization Efficiency | Good | Good | Very good | Very good |
NOx Generation | High | Moderate | None | None |
CO Decomposition | High | High | Efficient | Efficient |
Heat Recovery Efficiency | Low | High | Moderate | Very high |
Initial Costs | Moderate to high | High | Moderate | High |
Maintenance Costs | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to low |
Operating Costs | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
DFI is ideal for high VOC concentration and when a simple and reliable solution is needed, though it has high operating costs and environmental impact.
RTO offers a balance of high efficiency, energy recovery, and moderate operational costs, but its high initial investment may be prohibitive.
CCS/CATox/CO is a cost-effective solution for low-temperature applications, with low NOx emissions but efficient oxidation catalysts also play a decisive role.
RCO is highly efficient for VOC destruction and heat recovery, making it ideal for continuous operations, however, it requires the correct choice of oxidation catalyst and a high initial investment.
For large-scale, continuous operations with energy recovery needs, RCO and RTO are often preferred. For smaller-scale or highly specific VOCs, CCS/CATox/CO may be the most suitable option.
The raw material of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVD
Explore the viscosity grades and industrial appl
Discover how to prevent yellowing in textile fin
Contact: Tony Li
Phone: +86-13263299644
Tel: +86-13263299644
Email: sales@ecoviaet.com
Add: No 3 Youyi Road,Tangshan,Huantai,Zibo,China
We chat
