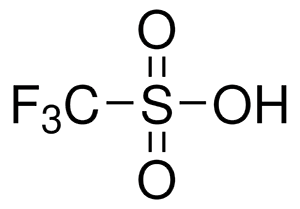
Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid (CAS 1493-13-6), also known as triflic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH,is considered difficult to work with for several reasons due to its extreme chemical properties. Here are the main challenges:
Triflic acid (CF3SO3H) is one of the strongest acids available, with a pka of around -14 at 25°C. Its high acidity can be corrosive to many materials and can cause severe burns to skin and eyes. This makes handling it dangerous without proper protective equipment and safe laboratory practices.
Triflic acid is highly hygroscopic (absorbs water from the air) and can readily form triflic acid anhydride when exposed to moisture. This reaction can be highly exothermic and potentially hazardous. As such, it must be handled under anhydrous conditions in a moisture-free environment, which can be cumbersome and require additional precautions.
Triflic acid is extremely corrosive to metals, glass, and many other materials commonly found in laboratory equipment. It can react with and damage these materials, requiring specialized, resistant containers and equipment for storage and handling, such as Teflon-lined or stainless steel containers.
While triflic acid itself is not classified as highly toxic, its derivatives and anhydrous forms may pose significant health risks. Prolonged exposure or improper handling can lead to respiratory, skin, or eye damage. In addition, triflic acid and its derivatives are persistent in the environment, and their disposal requires careful consideration to avoid contamination.
The anhydrous form of triflic acid (triflic acid anhydride) is particularly difficult to manage due to its strong tendency to react with moisture and form highly reactive intermediates. The anhydrous form must be handled under controlled environments, such as inert atmospheres (e.g., nitrogen or argon), and with dry solvents to prevent unwanted reactions.
Triflic acid and its derivatives are expensive and not always readily available in bulk. This can make it less practical for certain applications compared to other acids or catalysts that are easier to work with and more cost-effective.
Due to its strong acidity and reactivity, triflic acid requires specialized handling procedures, including proper containment, disposal, and neutralization methods. Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination or even dangerous chemical reactions.
Triflic acid must be stored in air-tight, moisture-proof containers to avoid contact with water and degradation. This adds complexity to its storage and transportation, requiring additional safety measures and resources.
In summary, triflic acid is challenging to work with because of its extreme acidity, high reactivity, moisture sensitivity, and potential toxicity. These characteristics necessitate specialized handling, storage, and disposal procedures to ensure safety and efficacy in its use, especially in sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals.
Contact: Tony Li
Phone: +86-13263299644
Tel: +86-13263299644
Email: sales@ecoviaet.com
Add: No 3 Youyi Road,Tangshan,Huantai,Zibo,China
We chat
